The Spectrum Display Window
This window displays the real or imaginary part of the resulting 2D spectrum (Zoom Mode).
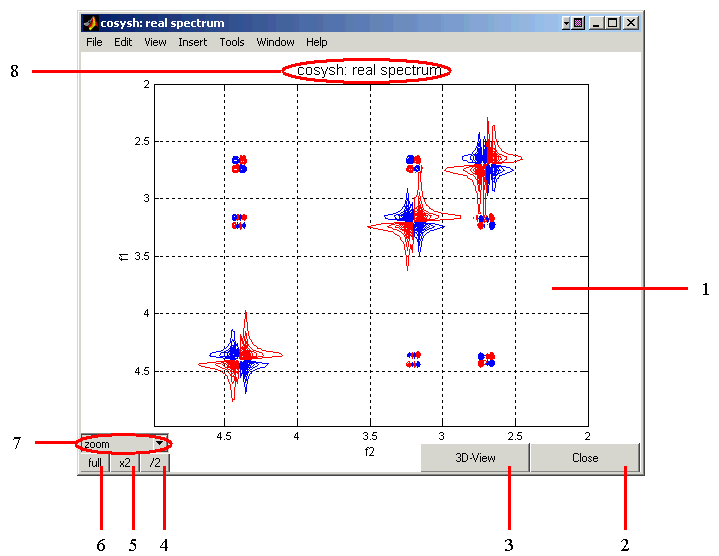
- 2D Spectrum: The spectrum is shown as contour levels, colored red for positive and blue for
negative levels. The axes are in ppm. By default, the range betwen the max and min signal amplitudes
in the spectrum is divided into 16 equidistant levels.
Spectrum Display/View Port Controls:
- Close: Clicking on this button will close the spectrum;
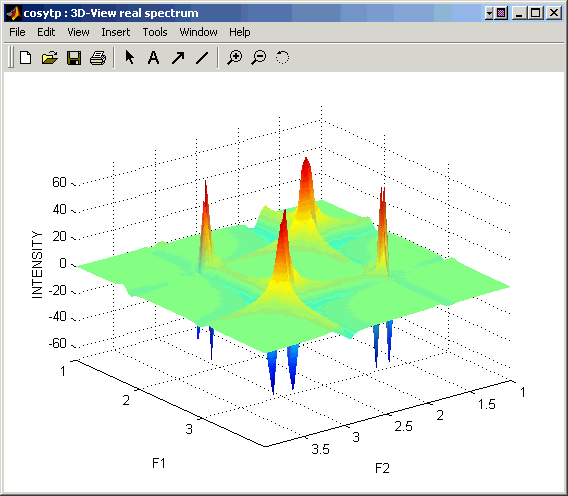
- 3D View: Display the current spectrum as a 3D surface (below); only zoomed-in part of the spectrum will be displayed;
- Reduce by 2: Two-fold reduction in the number of contour levels covering the range
{min,max} of signal intensities in the spectrum;
- Increase by 2: Two-fold increase in the number of contour levels covering the range
{min,max} of signal intensities in the spectrum;
- Full Spectrum: Display full spectrum, no zoom;
- Zoom/Section: This pull-dowm menu allows switching between the Zoom and Section
(see below) modes;
Also, in the Zoom Mode, the graph can be zoomed in using mouse (the procedure can be
repeated multiple times):
- select one corner of the desired region of the spectrum;
- press and hold the right mouse button and drag the mouse till it reaches the other
corner of the desired region;
- release mouse button, the zoomed-in window will be displayed automatically.
- Pulse Sequence/Spectrum: Indicated are the pulse sequence used to produce the spectrum and
whether the Real or Imaginary part of the spectrum is displayed.
Section Mode: This window allows analysis of 1D cross-sections of the 2D spectrum in both
F1 and F2 directions.
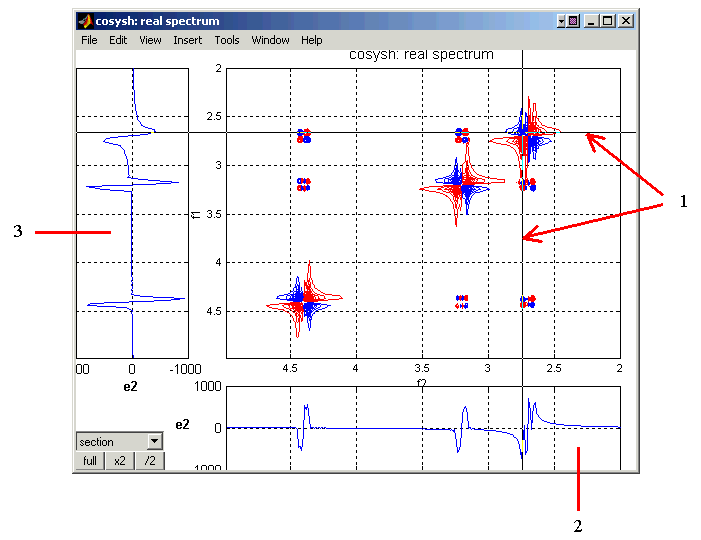
- Use mouse to select and click on the desired cross-section point (represented by the crossing thin
vertical and horizontal lines).
- The graph on the bottom displays a 1D cross-section through the spectrum in the F2 direction.
- The graph on the left displays a 1D cross-section through the spectrum in the F1 direction.
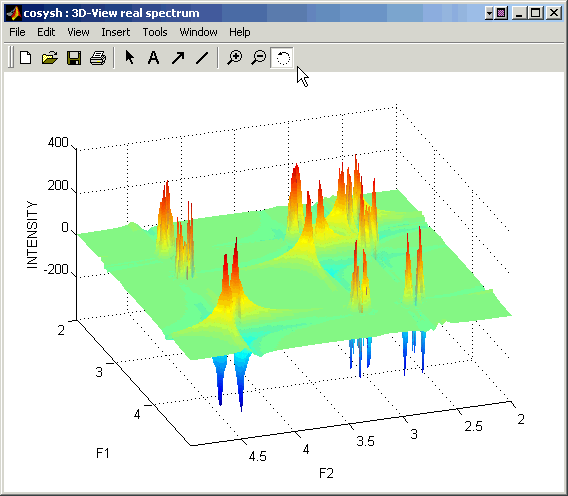
3D-view Mode: This window displays a user-selected region of the 2D spectrum as a 3D surface and
allows rotation of this surface to better represent its features.
You can change the appearence of the 3D surface representing your spectrum by typing the following command in the Matlab window (after the Matlab prompt):
shading faceted
Before typing this command make sure that the 3D-view panel is selected as the current active window. Here is an example of the faceted surface representation:
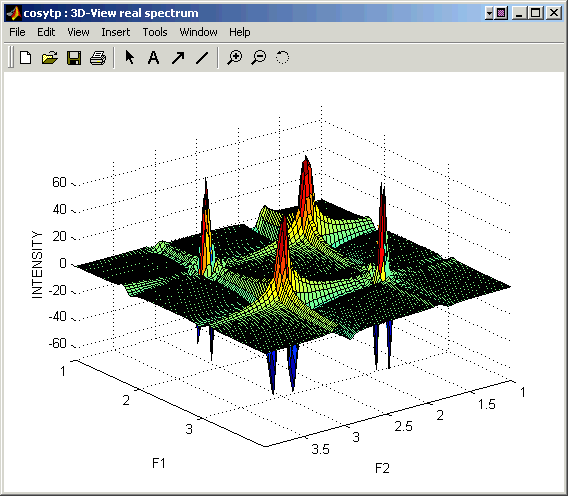
The "faceted" surface representation might not look good when the size of the plotted area exceeds 64 data points in any dimension.
To go back to the smooth representation of the surface type:
shading interp
 or close the 3D-view window and open it again.
or close the 3D-view window and open it again.
BACK TO DATA PROCESSING VINDOW
BACK TO VNMR MANUAL
Back to top
Page designed by David Fushman. Modified 12/28/2003.





